Malachi Hinds
The Great Storm of 1975
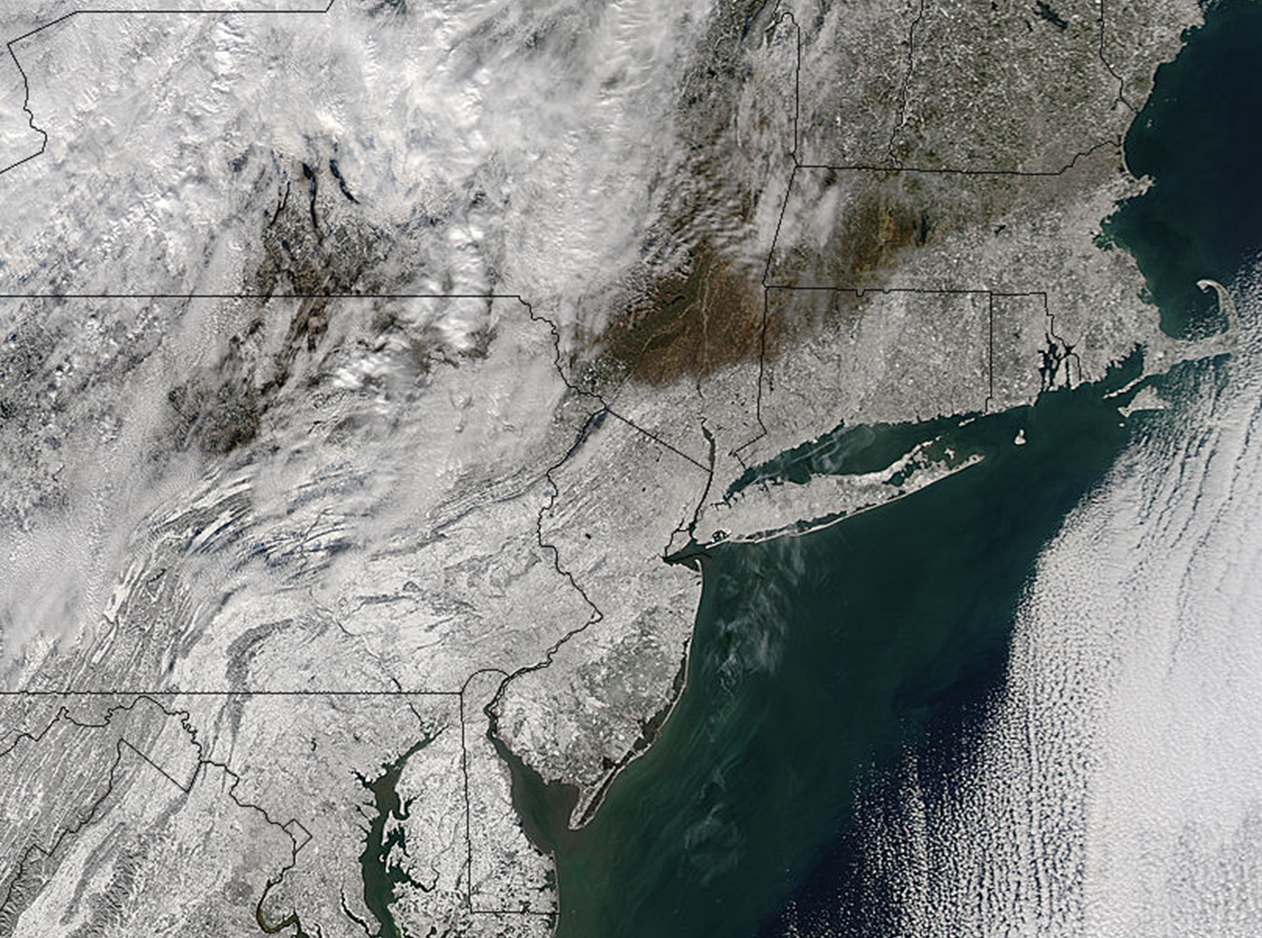
This storm occurred from January 9th-12th 1975. It is also known as “The Storm of the Century.”
In other parts of the country, it was called, “Super Bowl Blizzard,” (Vikings were playing Pittsburgh Steelers in New Orleans) or “The Great Storm of 1975.”The storm system originated over the Pacific Ocean on January 8. It crossed the Rocky Mountains and collided with both arctic air from Canada and warm tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico. Resulted in record low barometric pressure readings in the Midwest. This low-pressure system resulted in 42 tornadoes (Oklahoma, Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Arkansas, Texas, Indiana, Illinois, North Carolina, and Mississippi). Simultaneously,a powerful snowstorm gripped much of the Midwest
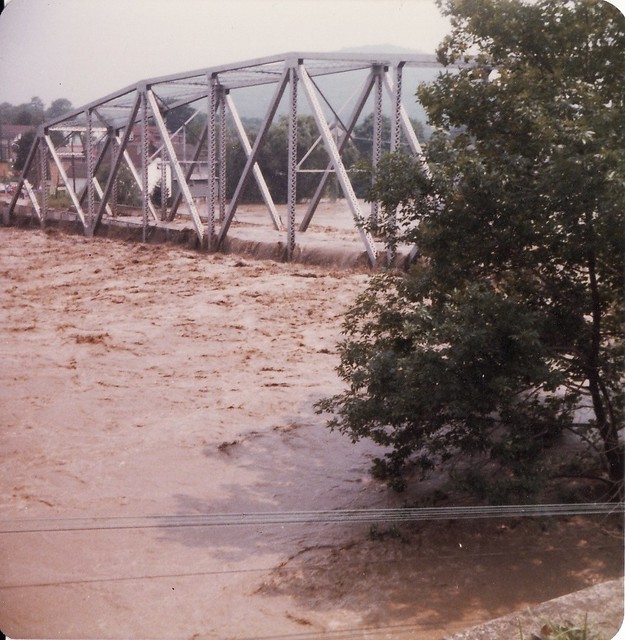
The storm also brought wind gusts of up to 90 mph and producing snowdrifts up to 20 feet high. The storm resulted in major damage to mainly Alabama and Mississippi. The storm costed a total of $63 million.
In other parts of the country, it was called, “Super Bowl Blizzard,” (Vikings were playing Pittsburgh Steelers in New Orleans) or “The Great Storm of 1975.”The storm system originated over the Pacific Ocean on January 8. It crossed the Rocky Mountains and collided with both arctic air from Canada and warm tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico. Resulted in record low barometric pressure readings in the Midwest. This low-pressure system resulted in 42 tornadoes (Oklahoma, Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Arkansas, Texas, Indiana, Illinois, North Carolina, and Mississippi). Simultaneously,a powerful snowstorm gripped much of the Midwest
The storm also brought wind gusts of up to 90 mph and producing snowdrifts up to 20 feet high. The storm resulted in major damage to mainly Alabama and Mississippi. The storm costed a total of $63 million.